Are You Living with Hip Pain?
The hip is called a ball-and-socket joint because the round ball-shaped head of the thighbone (femur) moves inside the cup-shaped hollow socket (acetabulum) of the pelvis. These bones are covered by cartilage, a layer of strong tissue that cushions the bones and allows smooth, easy movement of the joint.
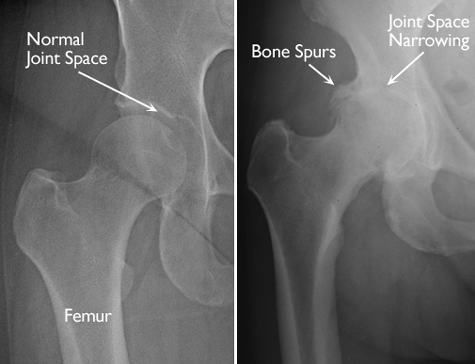
Degenerative joint disease (also known as DJD) can cause a loss of cartilage, resulting in bone-on-bone contact that may result in pain, swelling, and stiffness.
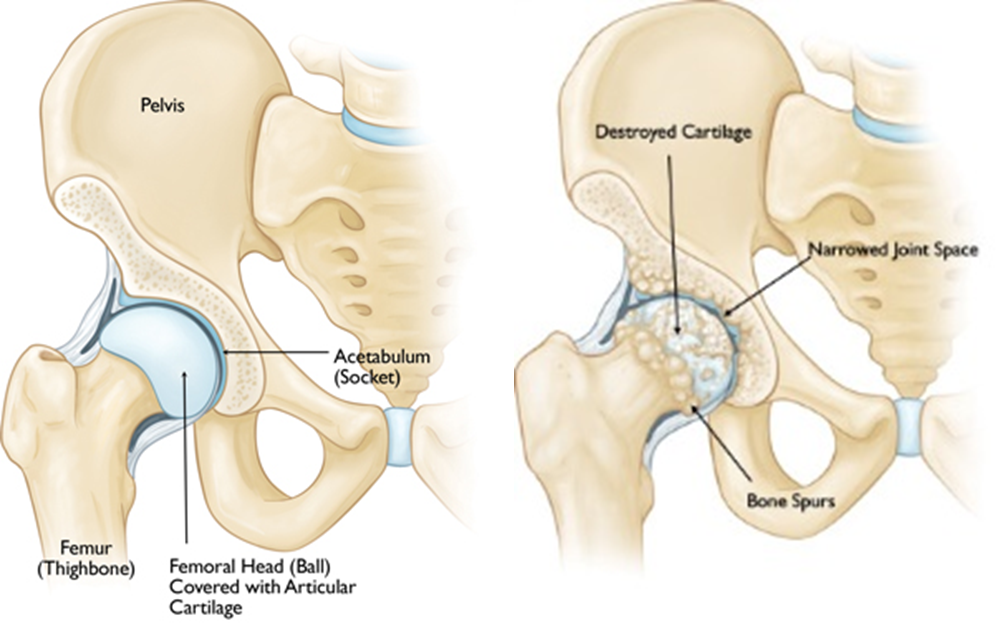
What causes degenerative joint disease?
The risk of developing symptomatic DJD is influenced by multiple factors such as age, gender, and inherited traits that can affect the shape and stability of your joints. Other factors can include a previous hip injury, repetitive strain on the hip, improper joint alignment, being overweight, and/or sports-generated stress placed on the hip joint.
There are different types of arthritis that may cause hip pain. An orthopedic surgeon or other physicians may diagnose:
- Osteoarthritis (OA), also called “wear-and-tear arthritis,” in which cartilage wears down over time, is the most common type of hip arthritis
- Post-traumatic arthritis, which results from a severe fracture or fracture or dislocation of the hip
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an inflammatory arthritis of the joints
- Avascular necrosis (AVN), a condition where the “ball” or femoral head has lost a healthy supply of blood flow, causing the bone to die and the femoral head to become misshapen
- Hip dysplasia, a condition in which bones around the hip did not form properly, which may cause misalignment of the hip joint
Cartilage has no nerves, so the break-down itself does not directly cause pain. However, the decreased “shock absorption” that results from a loss of cartilage causes increased stress to surrounding structures such as bones, muscles and the lining of the joint. This can lead to sudden “flares” of pain when these tissues get irritated.
Joint replacement surgery is considered a treatment option to relieve arthritis pain and restore function to the affected joint. Conservative treatment options are usually tried before surgery is recommended. Joint replacement surgery is recommended when pain is no longer well-controlled and joint damage significantly affects quality of life.
How do you know if you need a joint replacement? Ask yourself these questions:
- Have I tried medication and other conservative pain-relieving treatment options?
- Do I have unrelenting pain in the affected joint?
- Do I have significant difficulty with usual daily activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, cooking, cleaning, and more?
- Has my quality of life suffered due to arthritis pain and joint damage?
If you are answering “yes” to most or all of the questions, call our office at (801) 355-6468. You may be a candidate for joint replacement surgery.
